mhc class ii deficiency
The MHC II deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive primary immunodeficiency syndrome with increased susceptibility to respiratory and gastrointestinal infections failure to thrive and early mortality. MHC class II deficiency.
MHC class II deficiency is defined by the lack of MHC class II expression and autosomal recessive inheritance.
. The disease is primarily characterized by the absence of MHC class II molecules on the surfaces of immune cells. Three of seven 43 MHC class I-deficient and two of five 40 class II-deficient heart grafts were. MHC class II deficiency Molecular medicine A genetically heterogeneous AR immunodeficiency disease in which MHC II molecules are absent with altered gene regulation due to defects in several transactivating genes that regulate expression of MHC class II genes.
Madsen et al 1999. MHC class II molecules are pivotal for the adaptive immune system and guide the development and function of CD4 T-lymphocytes. Major histocompatibility complex MHC class II deficiency also known as bare lymphocyte syndrome type II is a rare autosomal recessive combined immunodeficiency and was first described in 1980s 1.
Major histocompatibility complex class II MHCII deficiency-also referred to as the bare lymphocyte syndrome BLS-is an autosomal recessive. Ad Flow Cytometry antibodies reagents for comprehensive cell analysis. MHC class II deficiency is a rare primary autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder PID.
The transplanted bone marrowcells do not react to the recipient since the recipient does not have MHC class II on cells Expression of MHC II -B lymphocytes -macrophages -dendritic cells -thymic epithelial cells loci. Approximately 100 patients with this disease have been reported to date. Patients with MHC class II deficiency have a severe defect of cellular and humoral immune responses.
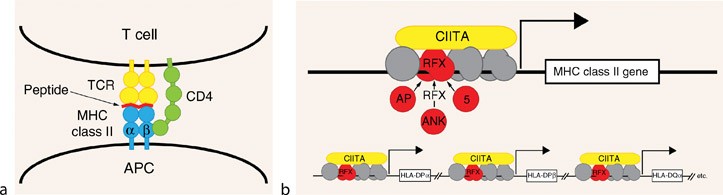
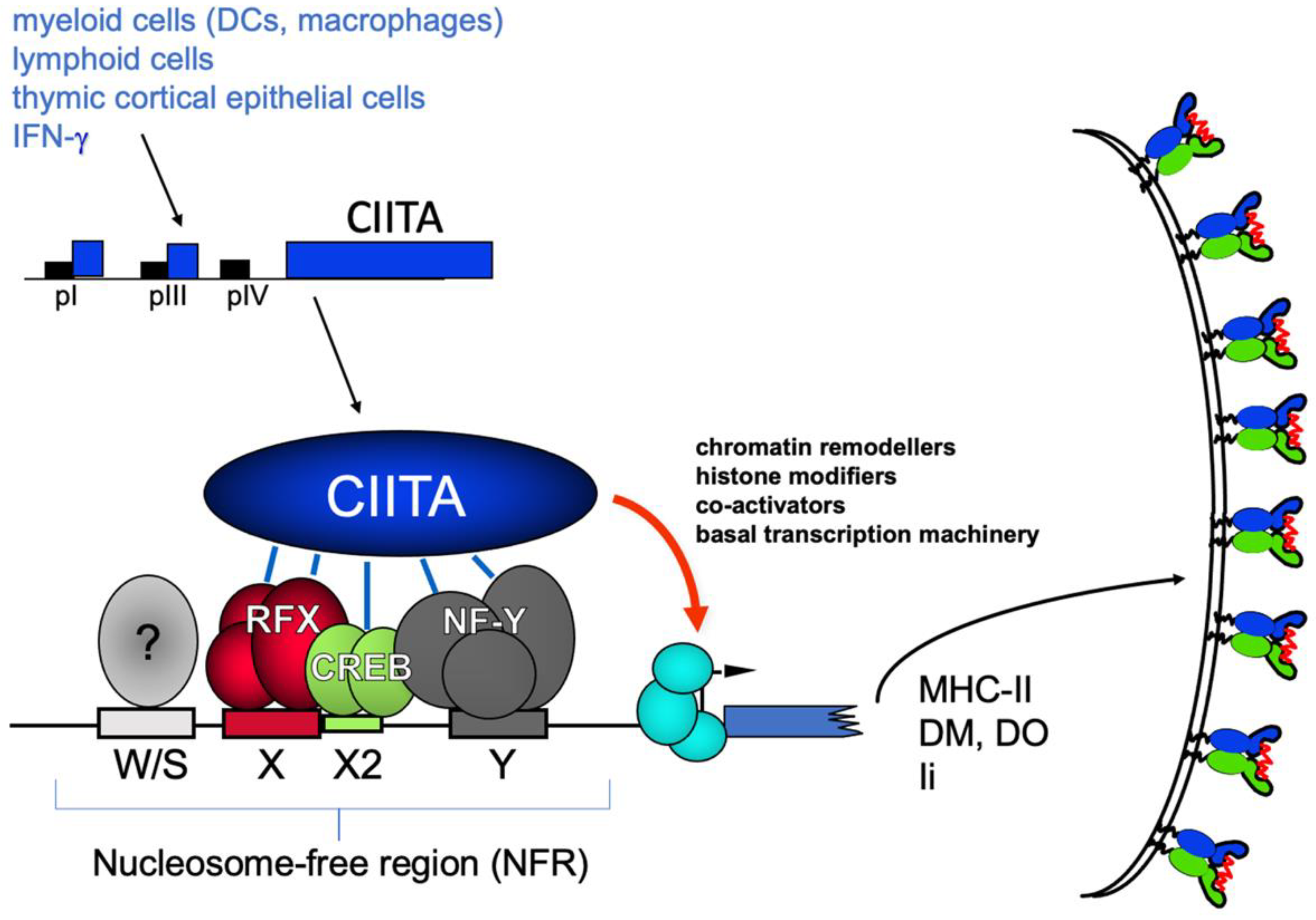
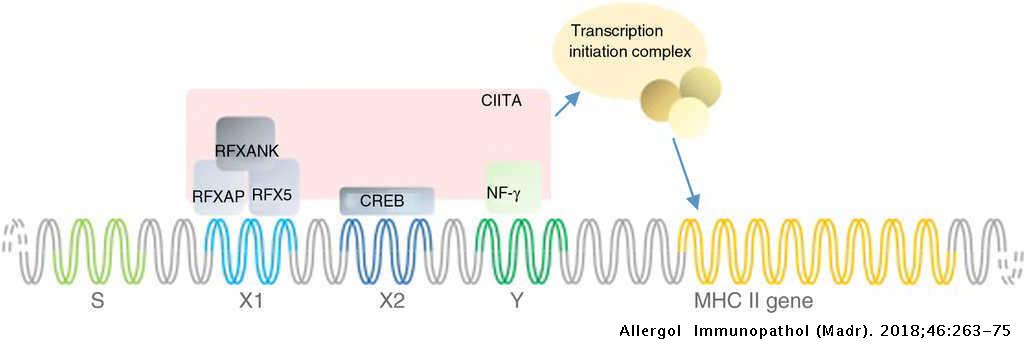
This immunodeficiency presents with a more severe phenotype than MHC class I deficiency. One type of MHC class II deficiency also called bare lymphocyte syndrome is due to mutations in the genes that code for transcription factors that regulate the expression of the MHC class II genes. MIM 209920 first described in the late 1970s.
MHC class II deficiency is caused by mutations of transcription factors that control MHC class II antigen expression by binding to the proximal promotors of the MHC. Grusby et al 1991. -Patients with 10 of normal MHC class I expression do not have an increased incidence of infections and are asymptomatic.
CD4 T cells are often decreased while CD8 T cells and B cells are present in normal numbers. DR DP DQ - defect in any of the 4 transcription factors involved with transcription of these loci leads to deficiency. The disease spectrum is quite broad ranging from asymptomatic to severe.
The affected genes encode. Patients presents early in infancy with a mild form of severe combined immunodeficiency SCID as they have increased susceptibility to pyogenic and opportunistic infections. MHC-II-deficient mice have been generated by targeted deletion of either the class II structural genes or the CIITA gene Chan et al 1993.
MHC Class II Deficiency Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome Type II Clinical definition an immunodeficiency syndrome possibly secondary to defects in DNA-binding regulatory molecules of the class II MHC promoter Presentation infections with viruses bacteria fungi protozoa. MHC class II deficiency is considered a single entity phenotypic condition in that patients have reduced or absent MHC class II expression and patients generally share some of the classic expected downstream immunologic and clinical consequences of this defect such as CD4 lymphopenia and impaired antigen specific responses. MHC class II deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder which is seen most often in patients from around the Mediterranean Sea.
Report of a novel mutation and special review. MHC class II deficiency major histocompatibility complexMHCII deficiency is a rare deficiency of MHC class II molecules and ultimately to a disruption of gene regulation. Chang et al 1996.
It results in the depletion of CD4 T cells and some immunoglobulin isotypes even though there are normal levels of both CD8 Cells and B cells present. This immunodeficiency is typically milder than MHC class II deficiency. Multiple biomarkers predictive of immunotherapy response and resistance have been proposed including but not limited to the expression of MHC-I and MHC class II MHC-II on tumor cells 12131415 transcriptome and cell signatures of immune activation 16171819 tumor mutation burden 20212223 favorable gut flora 24252627 and.
MHC class II deficiency is a rare primary autosomal recessive immunodeficiency disorder PID. The absence of cell surface MHC class I or class II resulted in significant prolongation of primary cardiac allograft survival. There is a higher prevalence in populations of North African origin.
MHC class II deficiency is a prototype of a disease of gene regulation. Patients suffering from this disease were first identified in the late 1970s and early 1980s 313536515590101102. Clausen et al 1998.
The disease is primarily characterized by the absence of MHC class II molecules on the surfaces of immune cells. Cosgrove et al 1991. And in these mice CD4 T cell development is severely impaired.
Defects in transacting regulatory factors required for expression of MHC class II genes rather than the genes themselves are responsible for the disease phenotype. Cited in 5 publications. MHC class II deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disease also known as bare lymphocyte syndrome type II.
Ad Available as HRP FITC PE Agarose and multiple 6 AlexaFluor conjugates. Among the primary immunodeficiencies MHC class II deficiency MHC-II deficiency is caused by the absence of MHC-II expression on the cell surface. Since then more than 70 patients have been clearly described.
MHC class II deficiency is a rare primary immunodeficiency disorder characterized by defective expression of MHC class II antigens. MIM 209920 first described in the late 1970s. Up to 10 cash back Major histocompatibility complex MHC class II deficiency is a genetic disease of autosomal recessive inheritance that is defined by absence or strong reduction of MHC class II HLA-DR DP DQ expression on peripheral blood cells 1.
Mhc Class Ii Deficiency Springerlink

Mhc Ii Molecules In Inflammatory Diseases Interplay Of Qualities And Quantities Trends In Immunology

The Location Of The Tap Genes In The Human Mhc Class Ii Complex Hla Download Scientific Diagram

Tumor Regulation Of Distal Mhc Class Ii ϫ Splenic Macrophage Download Scientific Diagram

A Genome Wide Multidimensional Rnai Screen Reveals Pathways Controlling Mhc Class Ii Antigen Presentation Cell
My Notes For Usmle Immunodeficiency Diseases Selective T Cells

Macroautophagy Proteins Control Mhc Class I Levels On Dendritic Cells And Shape Anti Viral Cd8 T Cell Responses Cell Reports
Ijms Free Full Text The Mhc Class Ii Transactivator Ciita Not Quite The Odd One Out Anymore Among Nlr Proteins Html

The Major Histocompatibility Complex Class Ii Abbey Jones Ppt Download

Mhc Class Ii Cell Autonomously Regulates Self Renewal And Differentiation Of Normal And Malignant B Cells Sciencedirect

3 Molecular Defect And Promoter Occupation In Mhc Class Ii Deficiency Download Scientific Diagram

Hla Dm An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Mhc Class Ii An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Mhc Class Ii Deficiency Report Of A Novel Mutation And Special Review Allergologia Et Immunopathologia
Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome Definition Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment

Targeted Complementation Of Mhc Class Ii Deficiency By Intrathymic Delivery Of Recombinant Adenoviruses Immunity

The Mhc Class I Dependent Antigen Presentation Pathway Intracellular Download Scientific Diagram